Thomas A. Barnico: Should Feds dictate rules on campus sexual misconduct? Beware
“My Eyes Clear Away Clouds” (collage), by Timothy Harney, a professor at the Montserrat College of Art, in Beverly, Mass.
From The New England Journal of Higher Education, a service of The New England Board of Higher Education (nebhe.org)
BOSTON
The U.S. Department of Education is poised to reverse Trump-era rules governing claims of sexual misconduct on campus. One could forgive weary college counsel for a case of vertigo: The Trump rules themselves reversed the Obama rules, and Biden’s 2021 nominee to enforce the rules—Catherine Lhamon—held the same office at the Education Department under Obama. In three years, the election of 2024 may bring yet another volte-face at the department. Even those who support the likely Biden changes may wonder: Is this any way to run a government?
As they ponder that question, frustrated counsel should note the primary source of the problem: the desire by serial federal officials to dictate hotly contested standards of student conduct for millions of students in thousands of colleges in a nation of 330 million people.
Some issues are better left to the provincials. As Duke Law professors Margaret Lemos and Ernest Young argue: “Federalism can mitigate the effects of [national] political polarization by offering alternative policymaking venues in which the hope of consensus politics is more plausible.” Delegation to state or local governments or, in education, to private actors, can “operate as an important safety valve in polarized times, lowering the temperature on contentious national policy debates.”
Of course, as Lemos and Young admit, “a federalism-based modus vivendi is unlikely to satisfy devoted partisans on one side or another of any divisive issue.” Such conflicts pit competing and compelling interests against one another.
In the Title IX context, parties fiercely debate the adequacy of protections for complainants and respondents alike: Does the respondent have a right to confront and cross-examine the complainant? Does the respondent have a right to counsel in their meeting with student affairs personnel? Do colleges and universities have to abide by a common definition of “consent” to intimacy in their student conduct manuals?
And, in polarized times, many will be unsatisfied with a patchwork of rules that apply state-by-state or college-by-college. Lost in this good-faith debate is the point that, even for issues with national effects, an oscillating national rule can cause more instability than an entrenched array of differing local rules.
Noted diplomat and scholar George F. Kennan aptly described the problem in Round the Cragged Hill: “The greater a country is, and the more it attempts to solve great social problems from the center by sweeping legislative and judicial norms, the greater the number of inevitable harshnesses and injustices, and the less the intimacy between the rulers and ruled. … The tendency, in great countries, is to take recourse to sweeping solutions, applying across the board to all elements of the population.” Central dictates, Kennan said, often show “diminished sensitivity of … laws and regulations to the particular needs, traditional, ethnic, cultural, linguistic and the like, of individual localities and communities.”
Of course, changes in administrations often bring changes in policy. Elections matter, and victors arrive with fresh ideas and an appetite for change. This is a highly democratic impulse; as U.S. Chief Justice William Rehnquist wrote: “A change in administration brought about by the people casting their votes is a perfectly reasonable basis for an executive agency’s reappraisal of the costs and benefits of it programs and regulations.”
Sometimes, such reappraisals will follow a reversal in the public current of the times. Where the new current runs strong and fast—and newly elected officials carry a decisive electoral mandate—a sweeping national solution may reflect a consensus view. But when electoral margins are slim, dangers lurk. When national executive and legislative power repeatedly changes hands by slim margins, policy changes may reflect not strong new currents but more of a series of quick, jolting bends.
The shifting procedural rights of the complainants and respondents in the Title IX misconduct hearings more resemble the latter. The abruptness of such changes grows when the commands flow not from a congressional act but by “executive order,” administrative “guidance,” or “Dear Colleague” letters that lack the procedural protections of a statute passed by both houses of Congress. Moreover, too-frequent changes in rules—whatever their procedural sources—have long been seen to create uncertainty, undermine compliance and lessen respect for law.
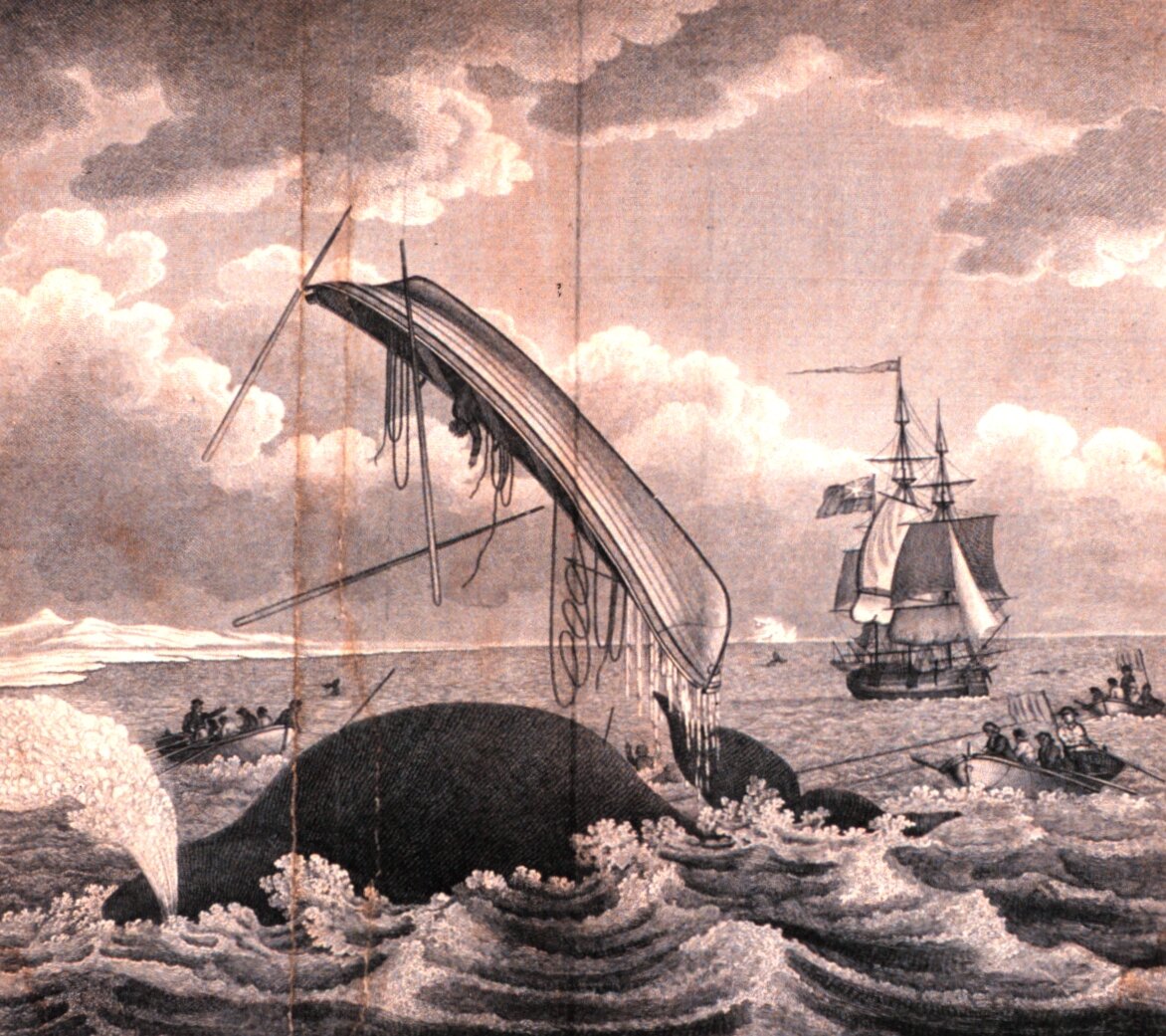
The options for beleaguered college counsel are few. Education Department rules apply to colleges because colleges desire federal funds. Few colleges wish to turn off the spout of the federal Leviathan. The masters they acquire are both the sovereign Leviathan of Hobbes and the whale dreamed by Herman Melville in Moby-Dick: a giant of the deep that pulls colleges to and fro, as if dragging them in a whaleboat on a “Nantucket Sleigh Ride.”
In our modern form of the tale, the whaleboat is the college, and the harpoon is its application for federal funding. The harpoon hits its rich federal target, but the prize brings conditions, represented by the attached rope. “Hemp only can kill me,” Ahab prophesizes. “The harpoon was darted; the stricken whale flew forward; with igniting velocity the line ran through the groove;—ran foul.” The rope—initially coiled neatly in a corner of the whaleboat—runs out smoothly until spent. Then it tangles, converting itself to a weapon more deadly than the harpoon. Bound by the rope—the conditions on federal funding—the college descends into the vortex.
Biden’s likely Title IX rules on student misconduct will pull college administrators to and fro again, whalers on a new, hard ride. The day that the federal government withdraws from the field seems distant; like Ahab, Education Department officials of both parties seem “on rails.” In the meantime, college counsel should brace for the latest chase and hope that they—like Ishmael—will live to tell the tale.
Thomas A. Barnico teaches at Boston College Law School. He is a former Massachusetts assistant attorney general (1981-2010).
“Nantucket Sleigh Ride”: Illustration of the dangers of the "whale fishery" in 1820. Note the taut ropes on the right, lines leading from the open boats to the harpooned animal.