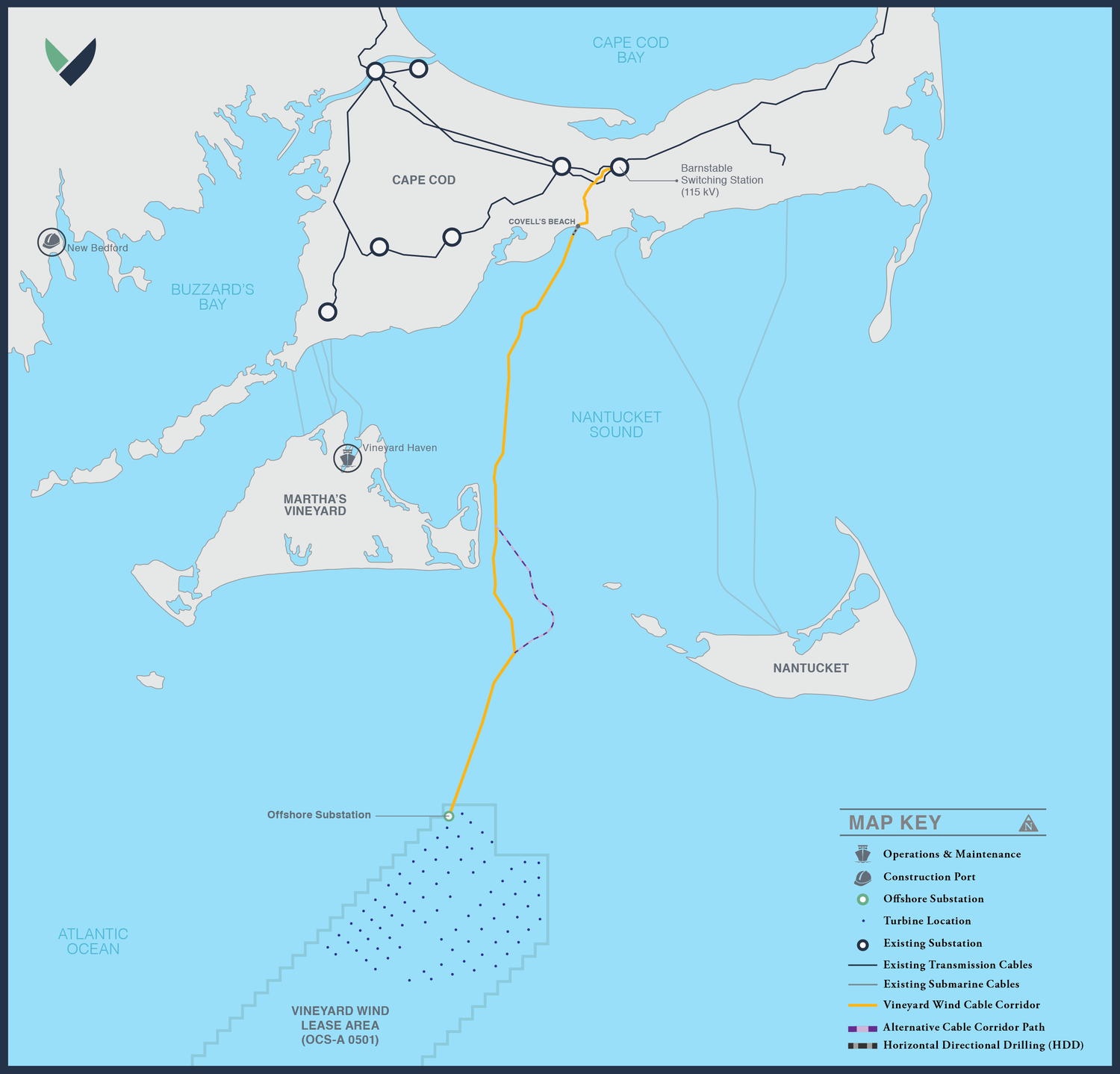
Closing on final approval of Vineyard Wind 1
From The New England Council (newenglandcouncil.com)
“Avangrid recently received the Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS) for Vineyard Wind 1 from the U.S. Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), the last step before a Record of Decision (ROD) that would jumpstart approval for the project to begin construction.
“A joint venture between Avangrid Renewables and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP), Vineyard Wind seeks to establish a massive offshore wind farm about 15 miles off the coast of Martha’s Vineyard.“Dennis V. Arriola, CEO of Avangrid, commented, “We are one step closer toward realizing this historic clean energy project and delivering cost-effective clean energy, thousands of jobs and more than a billion dollars in economic benefits to Massachusetts.” The project would generate electricity to power over 400,000 residences and businesses in Massachusetts, while also reducing electricity rates, carbon emissions, and creating new job opportunities.
“The New England Council looks forward to the progress Avangrid makes in developing this project for the region. Read more from the Hartford Business Journal and Avangrid’s press release.’’
Tim Faulkner: Is fossil-fuel-loving Trump regime trying to sabotage offshore wind?
Vineyard Wind is coming to terms with the fact that its wind project is behind schedule, as accusations of political meddling escalate.
On Feb. 7, the federal Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) released an updated permitting guideline that moved the facility’s likely completion date beyond Jan. 15, 2022 — the day the $2.8 billion project is under contract to begin delivering 400 megawatts of electricity capacity to Massachusetts.
Vineyard Wind is now renegotiating its power-purchase agreement with the three utilities that are buying the electricity. The company is also in discussions with the Treasury Department about preserving an expiring tax credit.
The delay is being caused by a holdup with BOEM’s environmental impact statement (EIS). A draft of the report was initially expected last year, but after the National Marine Fisheries Service and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration declined to endorse the report, it was pushed off until late 2019 or early 2020. Back then several members of Congress from Massachusetts claimed the delay was politically motivated.
BOEM now is predicting that the draft EIS won’t be ready until June 12, with a final decision by Dec. 18. The setback is significant because the draft EIS is being counted on to shape the mapping of other offshore wind facilities slated for the seven federal wind-energy lease areas off the coasts of Rhode Island and Massachusetts.
The Coast Guard recently released its Massachusetts and Rhode Island Port Access Route Study (MARIPARS). The report favors the grid design proposed by wind developers and discounted concerns about radar interference.
This navigational safety report also recommends that if the turbine layout in the entire Massachusetts and Rhode Island wind area is developed using “a standard and uniform grid pattern” then special vessel routing lanes wouldn’t be required.
The Coast Guard’s findings improve the prospect for development of all seven wind-energy lease areas. But the MARIPARS report and the draft EIS both require public comment periods and hearings.
Lars Pedersen, CEO of Vineyard Wind, said of the setback, “We look forward to the clarity that will come with a final EIS so that Vineyard Wind can deliver this project to Massachusetts and kick off the new U.S. offshore energy industry.”
This latest delay has again been criticized by members of the Massachusetts congressional delegation as a ploy by President Trump to demonstrate his aversion to wind energy and his favoritism for fossil-fuel companies.
On Feb. 5, two days before BOEM released the new timeline, Massachusetts’ two U.S. senators and seven members of Congress sent a letter to the U.S. Government Accountability Office expressing their outrage over Trump’s hypocrisy.
“Despite seeking expedited environmental reviews for numerous fossil fuel infrastructure projects, Trump administration officials in the Department of the Interior have ordered a sweeping environmental review of the burgeoning offshore wind industry, a move that threatens to stall or even derail this growing industry, and raises a host of questions for future developments,” according to the letter.
In a recent interview with the Vineyard Gazette, Rep. Bill Keating, D-Mass., whose district includes Martha’s Vineyard, said he believes BOEM planned to release the draft EIS much sooner, but stalled the report after political pressure from superiors in the Department of Interior or the Trump administration until after the presidential election in November.
“It’s clear to me that these are political decisions and not guided by wanting to mitigate environmental impacts,” Keating said.
When asked about the political interference, BOEM replied that the delays are caused by public comments that call for a more thorough review of a large and disruptive change to nearshore waters. Those comments cited the upsurge in new wind projects, an increase in the size of wind turbines used by Vineyard Wind, and potential conflicts with commercial fishing and navigation.
Meanwhile, investments in wind project port facilities continue along southern New England. Gov. Gina Raimondo has earmarked $20 million in her proposed budget for improvements to the Port of Davisville at the Quonset Business Park in North Kingstown, R.I. The work includes dredging, repair of an existing pier, and construction of a new pier.
Mayflower Wind, the next project after Vineyard Wind to win an energy contract from Massachusetts, recently announced its intention to make the New Bedford Marine Terminal its primary construction hub for its 804-megawatt project.
Tim Faulkner is an ecoRI News journalist.
Tim Faulkner: Future of offshore wind hangs on agency's report
Progression of expected wind turbine evolution to deeper water
From ecoRI News
The forthcoming report from the federal Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) on the cumulative environmental impacts of the Vineyard Wind project will determine the future of offshore wind development.
BOEM’s decision isn’t just the remaining hurdle for the 800-megawatt project, but also the gateway for 6 gigawatts of offshore wind facilities planned between the Gulf of Maine and Virginia. Another 19 gigawatts of Rhode Island offshore wind-energy goals are expected to bring about more projects and tens of billions of dollars in local manufacturing and port development.
Some wind-energy advocates have criticized BOEM’s 11th-hour call for the supplemental analysis as politically motivated and excessive.
Safe boat navigation and loss of fishing grounds are the main concerns among commercial fishermen, who have been the most vocal opponents of the 84-turbine Vineyard Wind project and other planned wind facilities off the coast of southern New England.
Last month, Rhode Island state Sen. Susan Sosnowski, D-New Shoreham and South Kingstown, gave assurances that the Coast Guard will not be deterred from conducting search and rescue efforts around offshore wind facilities, as some fishermen have feared.
“The Coast Guard’s response will be a great relief to Rhode Island’s commercial fishermen,” Sosnowski is quoted in a recent story in The Independent. “We have many concerns regarding navigational safety near wind farms, and that was the biggest.”
The anticipated release of the BOEM report coincides with President Trump’s efforts to weaken environmental impact reviews for all energy proposals, including wind, coal, and natural gas. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) reviews have slowed pipeline projects such as Keystone XL and, as of last summer, Vineyard Wind. Both industries praised the move to loosen environmental rules. Environmentalists, meanwhile, fear that the removal of terms such as “cumulative,” "direct," and "indirect" from NEPA’s directives will nullify future federal efforts to address the climate crisis.
Once the expanded environmental impact statement is released, BOEM will offer a comment period and hold public hearings
Stephens leaves Vineyard Wind
Barrington native and Providence resident Erich Stephens resigned at the end of 2019 from Vineyard Wind, a company he helped found in 2009 and is now co-owned by Avangrid and Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners. The original wind company was called Offshore MW. Prior to Vineyard Wind, Stephens was head of development for Bluewater Wind, one of the first U.S. offshore wind companies.
Stephens has considerable roots in Rhode Island. He attended Barrington High School and received his undergraduate degree from Brown University. He was founder and executive director of People’s Power & Light, now called the Green Energy Consumers Alliance. He was also a founding partner of Solar Wrights, a residential solar company that was based in Barrington and moved to Bristol. The company was later acquired by Alteris Renewables. Stephens also worked for two of Rhode Island’s first oyster farms.
More megawatts
New York plans to add 1,000 megawatts of offshore wind power to the 1,700 megawatts it awarded last summer to offshore wind projects that will deliver electricity to Long Island and New York City.
The state also announced it’s taking bids for $200 million in port development projects that will support the offshore wind industry.
The recent notifications are part of the state’s Green New Deal, which aims for 9 gigawatts of offshore wind by 2035 and 20 large solar arrays, battery-storage facilities, and onshore wind turbines in upstate New York. The state aims for 100 percent renewable energy by 2040.
The latest offshore wind projects consist of the 880-megawatt Sunrise Wind facility, developed by Ørsted and Eversource Energy, to power Manhattan. Long Island will receive up to 816 megawatts from the Empire Wind facility, developed by Equinor of Norway.
Pricing for the projects hasn’t been made public.
Offshore leader
Based in Denmark, Ørsted is the early leader in the size and number of U.S. offshore wind projects. Ørsted was awarded the 400-megawatt Revolution Wind project for Rhode Island. It’s also developing the 1,100-megawatt Ocean Wind facility in New Jersey, a demonstrations project in Virginia, and projects in Connecticut, Delaware, Massachusetts, and Maryland. The company acquired Providence-based Deepwater Wind in 2018 for $510 million.
Ocean Wind, New Jersey’s first offshore wind project, and the 120-megawatt Skipjack Wind Farm off Maryland will use General Electric’s huge 12-megawatt Haliade-X turbines. The 853-foot-high turbines are the tallest in production and have twice the capacity of the 6-megawatt GE turbines now spinning off Block Island, which are 600 feet tall.
Tim Faulkner is a journalist with ecoRI News.